Summary
-
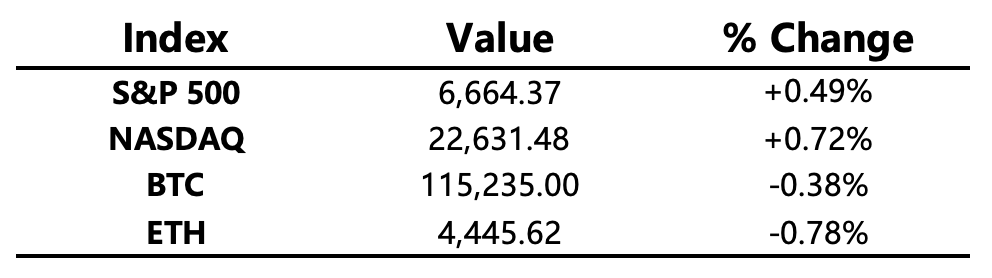
Macro Environment: U.S. stocks rose again on Friday, posting two consecutive gains after the rate cut. The three major U.S. stock indexes continued to reach new highs, while the previously strong small-cap stocks pulled back from recent highs.
-
Crypto Market: Bitcoin failed to hold above the $117,000 resistance level, showing a choppy downward trend. ETH remained weak, and the altcoin market cap dominance fell by 0.4%. Excluding ETH, altcoin market cap dominance dropped by 0.1%. Despite the downward trend in BTC and ETH, altcoins overall remained stable, with some sectors such as Perp DEX showing strong performance.
-
Project Developments
-
Hot Tokens: ASTER, WLFI
-
ASTER/AVNT: The Perp DEX sector gained strong momentum, with ASTER and AVNT surging 1425% and 177% respectively in the past 7 days, with their contract trading volumes surpassing BTC.
-
WLFI: WLFI implemented a 100% fee buyback and burn proposal, rising 13% in the past 7 days. Trading volume surged in Korea, ranking WLFI third on Upbit.
-
SUN: Justin Sun announced that all SUNPerp revenue will be used for SUN buybacks.
-
NEAR: Near AI will launch a crypto chat platform later this month or early next month.
-
ROIN: Ronin Treasury will start a RON buyback on September 29, equivalent to about 1.3% of the circulating supply.
-
Mainstream Asset Changes
-
Crypto Market Fear & Greed Index: 45 (49 a day ago), level: Fear
Today’s Outlook
-
Robinhood will officially be included in the S&P 500 Index
-
KBW 2025 kicks off
-
ID unlocks 6.30% of circulating supply, worth about $12.9 million
Macroeconomics
-
Bank of Japan keeps interest rates unchanged
-
A temporary spending bill aimed at avoiding a U.S. government shutdown passed the House but failed in the Senate
Policy Trends
-
U.S. Treasury Department launches GENIUS Act stablecoin regulatory framework
Industry Highlights
-
Michael Saylor once again released Bitcoin Tracker info, may disclose additional purchases next week
-
Ethereum mainnet Fusaka upgrade tentatively scheduled for December 3, 2025
-
Bitcoin mining difficulty increased by 4.63% to 142.34T, reaching another all-time high
-
Custodian BitGo filed for IPO, with H1 revenue of nearly $4.2 billion and profit of over $12 million
-
FTX to launch third round of creditor repayments, totaling $1.6 billion
-
Ethereum ecosystem stablecoin supply reached $166 billion, a new all-time high
Further Reading:
According to Chaincatcher, citing data from CloverPool, the Bitcoin network recently underwent a difficulty adjustment at block height 915,264. The difficulty increased by 4.63%, reaching a new all-time high of 142.34 T. This not only reflects the current health of the Bitcoin network but also highlights the increasingly fierce competition and challenges within the mining sector.
What is Mining Difficulty?
To understand the significance of this data, we first need to grasp what mining difficulty is.
Bitcoin mining is a "puzzle-solving" process: miners use specialized computers (mining rigs) to perform high-intensity hash calculations, attempting to find a random number (Nonce) that meets a specific condition to generate a new block. This "condition" is determined by the mining difficulty. The higher the mining difficulty, the more complex the calculations miners must perform, and the lower their probability of finding the correct answer.
The brilliance of the Bitcoin protocol lies in its automatic adjustment mechanism, which ensures that new blocks are generated at a stable rate of approximately 10 minutes per block. Every 2016 blocks (about two weeks), the network adjusts the difficulty based on the actual speed of block generation over that period.
-
If new blocks are generated too quickly (averaging less than 10 minutes), it means more miners and hash power have joined the network, so the network will increase the difficulty to slow down block generation.
-
If new blocks are generated too slowly (averaging more than 10 minutes), it means some miners have left or hash power has decreased, so the network will decrease the difficulty to speed up block generation.
This latest 4.63% increase in difficulty means that over the past two weeks, the Bitcoin network's overall computing power (i.e., hash rate) has significantly grown, and miners have been finding new blocks faster than expected. As a result, the network automatically raised the difficulty to maintain its preset 10-minute block time.
The Deeper Meaning Behind the Difficulty Increase
This new difficulty record is more than just a change in numbers; it carries several deeper implications:
-
Enhanced Network Security
Mining difficulty is directly correlated with the security of the Bitcoin network. Higher difficulty means more computing power is dedicated to mining, which makes the cost of launching a 51% attack on the network prohibitively expensive. This makes the Bitcoin blockchain more resistant to manipulation, thereby strengthening the entire network's robustness and trustworthiness. A continuously rising difficulty is a positive sign for the network's long-term health.
-
Challenges and Opportunities for Miners
For miners, the increase in difficulty is a double-edged sword.
-
Challenges: Higher difficulty directly leads to increased computational requirements and electricity consumption, while the block reward (currently 3.125 BTC) remains constant. This means that the output per unit of hash power decreases, and mining costs rise, squeezing miners' profit margins. Those with older equipment and high electricity costs will face greater pressure to survive and may be forced to shut down their operations.
-
Opportunities: The rising difficulty also accelerates industry consolidation. Only those miners with more efficient rigs (like the latest ASIC miners), access to cheaper electricity, and superior operational management can survive this competition. This pushes the entire mining industry toward greater professionalization and scale, and incentivizes technological innovation to find more efficient energy solutions.
-
Market Sentiment and the Mining Ecosystem
The continuous increase in Bitcoin mining difficulty, to some extent, reflects market optimism about the future of cryptocurrency. If miners expect Bitcoin's price to rise, they are willing to invest more capital into buying equipment and expanding their scale, even if profits are slim in the short term. This behavior itself indicates that large capital and professional mining companies have strong confidence in the future. Furthermore, this also drives the flourishing of the entire mining ecosystem, including mining pools, hardware manufacturers, and energy companies.
Behind every new difficulty record is a relentless game of hash power, cost, and efficiency between miners worldwide. This game not only continuously fortifies the security of the Bitcoin network but also serves as a vibrant testament to the vitality and prospects of the entire cryptocurrency industry. As technology advances and more players enter the space, we have every reason to believe that Bitcoin mining competition and difficulty will continue to climb, providing a solid foundation for the network's stability and development.














