Introduction: From Centralized Giants to User Sovereignty
We are living in a digital age dominated by internet giants. From social media to e-commerce and content distribution, our data, digital assets, and even our digital identities are highly concentrated in the hands of a few centralized platforms. While this model has brought unprecedented convenience, it has also been accompanied by issues such as privacy breaches, data misuse, content censorship, and platform monopolies.
However, a revolution driven by blockchain technology and cryptocurrency is quietly underway. It aims to reshape the internet's underlying structure, returning power from centralized entities to users. This, is what we call Web3. In the cryptocurrency field, Web3 is not just a concept; it is actively building a decentralized, transparent, and truly user-owned digital future through practical applications and protocols.
This article will delve into the essence of Web3 in the cryptocurrency domain, its core pillars, and key applications, anticipating how it will lead the internet into the next Web3 era.
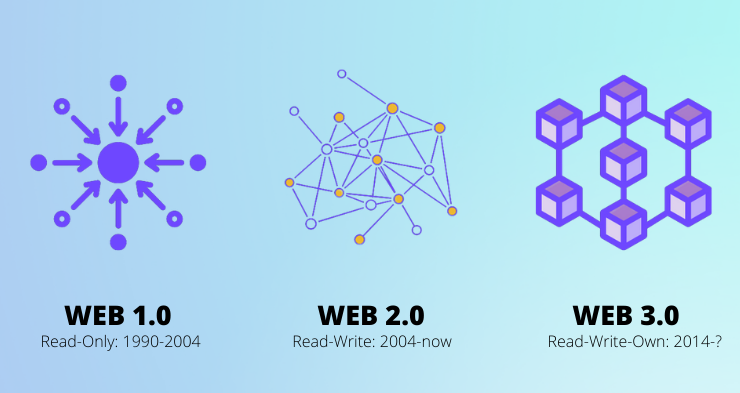
I. The Evolution of the Internet: A Paradigm Shift from Web1, Web2 to Web3
To deeply understand the implications of Web3, we must place it within the grand narrative of the internet's evolution:
-
Web1.0 (The Read-Only Web):
-
Era: Mid-1990s to early 2000s.
-
Characteristics: The Internet's nascent stage, primarily composed of static web pages. Users acted as passive consumers of information, Browse news sites and corporate homepages. Content creation and publishing rights were held by a small number of organizations and individuals. This phase of the internet was largely "one-way broadcasting."
-
Keywords: Portals, static information, information retrieval.
-
-
Web2.0 (The Read-Write Web / Social Web):
-
Era: Mid-2000s to present.
-
Characteristics: Emphasized User-Generated Content (UGC) and high interactivity. Social media (e.g., Facebook, Twitter), video-sharing platforms (YouTube), e-commerce platforms (Amazon, Taobao), and blogs flourished. Users could actively participate in creating, sharing, and interacting with content.
-
Advantages: Greatly enriched internet content, fostered global connection and communication, and spawned powerful platform economies.
-
Underlying Problems: Despite users creating value, data and power became highly concentrated in the hands of a few internet giants. These centralized platforms controlled vast amounts of user data, dictated content distribution rules, could easily censor or block content, and even stripped users of true ownership over digital assets created on their platforms (e.g., game accounts, virtual currency). Your digital footprint and personal privacy largely did not belong to you. This is the core contradiction of Web2.
-
Keywords: Social media, User-Generated Content, platform economy, data centralization, privacy concerns.
-
-
Web3.0 (The Read-Write-Own Web / Decentralized Web):
-
Era: Emerging now, built on blockchain and cryptographic technologies.
-
Characteristics: The core philosophy of Web3 is decentralization and user ownership. It aims, through technological means, to empower users to truly own and control their data, digital identity, and digital assets. Web3 strives to build a more open, transparent, trustless internet governed by its users.
-
Transformative Aspect: Web3 directly addresses the drawbacks of Web2's centralization, seeking to shift control from a few platforms to the broader user base and communities, allowing everyone to benefit from the value they create. Web3 is not merely a technological iteration but a paradigm shift in its very concept.
-
Keywords: Decentralization, user ownership, blockchain, cryptocurrency, NFT, smart contracts, DAO.
-
II. The Core Principles of Web3: Building the Foundation of the Next Generation Internet
Web3 is not a single technology but the embodiment of a set of core principles and technological ensembles that define its fundamental difference from traditional internet:
1.Decentralization:
-
The Soul of Web3: This means no single centralized entity (e.g., company, government) can control the entire network, data, or applications.
-
Data is stored across a distributed network of nodes, and application logic is deployed on a blockchain. This provides Web3 networks with stronger censorship resistance, making them resilient to single points of attack or shutdown. In the Web3 world, power is no longer concentrated.
2.User Ownership:
-
In Web3, users truly own and control their data, digital identity, and digital assets.
-
There's no need to rely on third-party platforms for identity verification or data storage. Users manage everything through their own cryptographic wallets (holding private keys), and data is stored on the blockchain, accessible, transferable, and even monetizable at any time. This is a fundamental disruption of Web2's "platform owns data" model by Web3.
3.Open & Permissionless:
-
Web3 protocols and underlying technologies are open and transparent; anyone can view and audit the code.
-
Anyone can freely participate in Web3 networks, whether as a user, developer, or node operator, without needing approval or authorization from any centralized entity. This openness greatly fosters innovation and prosperity within the Web3 ecosystem.
4.Trustless:
-
Interactions and transactions in Web3 primarily rely on smart contracts and the underlying blockchain's cryptographic assurances.
-
This means users do not need to trust any third-party intermediaries (like banks or payment gateways); transactions are automatically executed by code, and the results are verifiable and immutable. This "code is law" characteristic is key to the efficient and secure operation of Web3.
5.Native Payments:
-
Web3 integrates digital assets and payment functionalities at the underlying protocol layer.
-
Users can directly transfer value within applications without traditional banking or payment gateways. This significantly reduces transaction costs, improves efficiency, and lays the foundation for new economic models within Web3.
6.Interoperability:
-
One of Web3's goals is to break down the data silos prevalent in Web2 platforms.
-
Through standardized protocols and cross-chain technologies, Web3 aims to achieve seamless flow and interaction of assets and data across different blockchains and applications, thereby building a more coherent and integrated digital world.

III. Web3's Realization and Empowerment in the Cryptocurrency Field
The core principles of Web3 are not abstract concepts; they are concretely realized and widely applied through technological innovations in the cryptocurrency field
1.Blockchain: The Foundation of Web3
-
How it enables decentralization: Blockchain provides a decentralized, transparent, and immutable distributed ledger, ensuring the integrity and security of data and transactions. All Web3 applications run on such decentralized networks, rather than centralized servers. Bitcoin and Ethereum are the original and most typical foundational Web3 blockchains.
-
Data Storage & Verification: User data, asset states, and application logic are recorded on the blockchain and verified through network consensus mechanisms, ensuring the integrity and tamper-proof nature of Web3 data.
2.Cryptocurrencies/Tokens: Web3's Economic Bloodline and Vehicle for User Ownership
-
Proof of Ownership: Users control their wallets with private keys, and the cryptocurrencies and tokens within represent their digital asset ownership in the Web3 ecosystem. This ownership is cryptographically secured, not merely authorized by a platform.
-
Value Transfer: Cryptocurrencies serve as the core medium for native payments and value transfer in Web3, eliminating the need for intermediaries like banks.
-
Economic Incentives: Token economic models incentivize users to participate in the maintenance, governance, and content creation of Web3 networks, such as earning yields through staking or rewards for providing liquidity.
-
Governance Rights: Governance tokens give holders voting rights, enabling them to participate in the decentralized governance of Web3 protocols and projects, truly exercising their rights as owners.
3.Smart Contracts: Web3's Automated Logic
-
Trustless Agreements: Smart contracts are automated code deployed on a blockchain that executes automatically when predefined conditions are met, without third-party intervention. This establishes a "code is law" trust mechanism in Web3.
-
Core of dApps: Almost all Web3 decentralized applications (dApps) rely on smart contracts to define their core logic and business rules. From simple token transfers to complex financial protocols, everything is driven by smart contracts.
4.Non-Fungible Tokens (NFTs): Web3's Proof of Unique Digital Asset Ownership
-
Unique Digital Ownership: NFTs are unique, non-interchangeable cryptographic tokens used to represent exclusive digital asset ownership.
-
Applications: In Web3, NFTs are widely used in digital art, collectibles, in-game assets (e.g., virtual land, character skins), digital identity credentials, ticketing, and more. They bring scarcity and verifiable ownership to the digital world. NFTs are a crucial component of the Web3 creator economy and the metaverse.

(Source: Medium)
IV. Core Applications and Ecosystems of Web3 in the Cryptocurrency Field
Web3 is not just theoretical; it has already spawned a series of disruptive applications in the cryptocurrency field, reshaping how we interact with the digital world:
1.Decentralized Finance (DeFi): Web3's Financial Future
-
Core Concept: DeFi aims to build a financial system without banks, brokers, or other centralized intermediaries, leveraging Web3 technologies and smart contracts.
-
Services: It offers various financial services like lending, borrowing, trading (Decentralized Exchanges - DEX), and insurance. Users interact directly through smart contracts, greatly enhancing transparency, efficiency, and accessibility. DeFi is one of the most mature and largest application areas within Web3.
2.Decentralized Applications (dApps): Web3's Open Software Ecosystem
-
Operating Model: DApps are Web3 applications running on a blockchain, with their backend logic and data storage deployed on decentralized networks.
-
Diverse Types: Beyond DeFi platforms, Web3 dApps include decentralized social media (e.g., Lens Protocol, aiming to reshape Web3 social interactions), content platforms (e.g., Steemit, where creators earn directly), storage solutions (e.g., Filecoin, providing decentralized storage), and decentralized identity verification systems. These Web3 applications aim to break down the centralized barriers of traditional apps.
3.Decentralized Autonomous Organizations (DAOs): Web3's New Paradigm for Collaboration
-
Governance Model: DAOs are a new type of organization in Web3, with rules defined by smart contracts and governance conducted through token holder voting.
-
Democratization: They allow community members globally to jointly own and manage projects, enabling transparent and flat decision-making processes. DAOs are a central embodiment of the Web3 spirit, representing a new paradigm for organizational collaboration.
4.Metaverse and Web3 Gaming: Web3's Immersive Experience and Ownership Economy
-
Digital Asset Ownership: Web3 technology is fundamental to building a true metaverse. Through NFTs, users can own virtual land, clothing, items, and other digital assets within the metaverse, with verifiable, tradable, and cross-platform interoperable ownership.
-
Play-to-Earn Model: Web3 games (or blockchain games) introduce the "Play-to-Earn" model, allowing players to convert their time and effort invested in games into monetizable digital assets, granting them true ownership and economic incentives. This is a prime example of how Web3 empowers users and redefines the gaming industry's economic model.
V. The Immense Potential and Challenges of Web3
Web3 paints an exciting future, but its development is not without its hurdles.
5.1 The Immense Potential of Web3:
-
User Empowerment: Web3 fundamentally returns data and asset ownership to users, breaking the monopoly and control of Web2 platforms over data.
-
Transparency and Security: The transparency and cryptographic security of blockchain greatly enhance trust in Web3 transactions and interactions, reducing fraud risk.
-
Censorship Resistance: The decentralized nature of Web3 makes applications and data harder to unilaterally shut down or censor, safeguarding freedom of speech and information in the digital world.
-
Innovation and Inclusivity: The open and permissionless nature strongly encourages global developers to participate in Web3 ecosystem innovation, and can reach users outside traditional financial systems, achieving greater financial inclusion.
-
New Economic Models: Web3 has spawned disruptive models like "Play-to-Earn," "Learn-to-Earn," and "Create-to-Earn," greatly stimulating user participation and building a fairer value distribution system.
5.2 Challenges Facing Web3:
-
Technical Scalability: Current blockchain transaction throughput (TPS) and confirmation speeds remain bottlenecks, limiting the widespread adoption of Web3 applications. Although Layer 2 solutions and new high-performance public chains are developing, they still need time to mature.
-
User Experience (UX): The barrier to entry for Web3 applications is relatively high (e.g., managing private keys, understanding gas fees, complex dApp interfaces), making them user-unfriendly for the general public, which is one of the biggest obstacles to Web3's mainstream adoption.
-
Regulatory Uncertainty: Regulatory frameworks for cryptocurrencies and Web3 are still evolving across various countries, making legal compliance a significant challenge that could impact the future development and popularization of Web3 projects.
-
Security Risks: Smart contract vulnerabilities, improper private key management, and phishing attacks remain major security concerns in the Web3 space. The decentralized nature of Web3 also means that once assets are lost, they are almost impossible to recover, requiring users to bear more responsibility for self-custody.
-
Environmental Impact: Some underlying Web3 technologies (e.g., Proof-of-Work, PoW) consume vast amounts of energy, raising environmental concerns, although transitions to more energy-efficient mechanisms like Proof-of-Stake (PoS) are underway.
Conclusion: Web3 – Embracing a Cryptocurrency-Driven Digital Future

Web3 is more than just a technological concept; it represents a profound paradigm shift in the Internet's evolution. It aims to build a more open, fair, and user-driven digital future through cryptocurrency and blockchain technology. It decentralizes power from centralized entities to network participants, empowering users with true ownership over their digital assets and identities.
Although Web3 is still in its early stages of development and faces numerous technological and adoption challenges, the decentralized vision it portrays, along with the immense innovation and application potential it demonstrates in the cryptocurrency field, heralds the next Web3 wave for the internet and the digital economy. Embracing Web3 means embracing a future filled with infinite possibilities and greater user value.












